
The cortex consists of a small, outer permanent zone and a large, inner fetal zone.

Concurrently, cells destined to form the permanent or adult adrenal cortex proliferate and eventually envelop the fetal cortex.Īt birth, the adrenal glands are 10–20 times larger than the adult gland, relative to kilograms of body weight. The adrenal medulla is formed from the neural crest cells that migrate to the medial aspect of the cortex during the seventh week of fetal development. The fetal cortex begins its development in the 5-week-old fetus as a collection of large, acidophilic cells located between the root of the dorsal mesentery and the developing gonad.
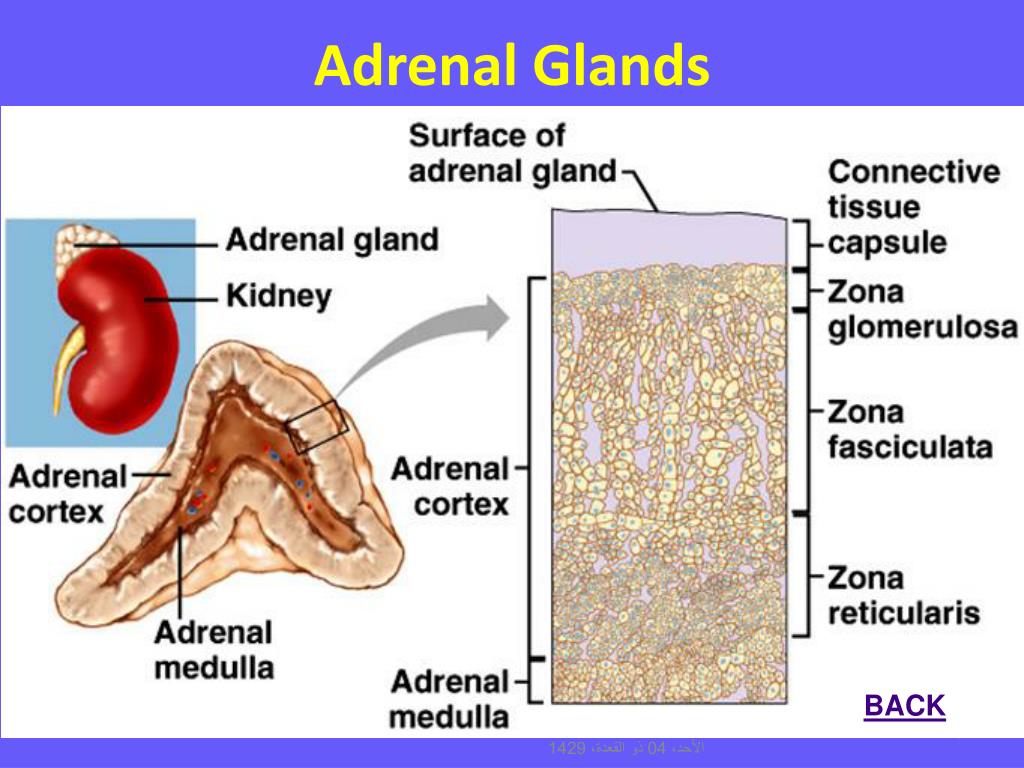
The adrenal cortex is derived from the mesoderm lining the posterior abdominal wall. In most persons, the left adrenal vein drains into the inferior phrenic vein before emptying into the left renal vein in some, it enters the left renal vein directly. The short right adrenal vein drains directly into the inferior vena cava. Blood flow proceeds from the subcapsular region toward the central (medullary) portal vein. The blood supply to the adrenal consists of numerous arteries that usually arise from the aorta, the inferior phrenic arteries, and the renal arteries. In the zona reticularis, the cells are arranged in alveolar patterns, with vascular sinuses. The clear cells of the zona fasciculata gradually blend with the more lipid-poor cells of the zona reticularis. Most of the adrenal cortex is composed of the zona fasciculata, which is characterized by clear, large, lipid-rich cells arranged in parallel cords, with long columnar vascular sinuses interposed. The subcapsular zona glomerulosa consists of discontinuous clusters of relatively small, lipid-poor, compact cells. The adult cortex is divided into three histologic zones: zona glomerulosa, zone fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The cortex accounts for 80% and the medulla 20% of the weight of the adult gland.

The increase in size at autopsy has been attributed to the stress of antecedent illness. In autopsy series, the average weight is 6 g. After sudden death, the average weight of the adrenal in healthy persons is 4 g. They are surrounded by a capsule and are located at the upper pole of the kidneys. Normal adrenal glands are paired, pyramidally shaped, yellow-brown convoluted organs surrounded by fat.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
